Dermatitis in dogs is an inflammation of the skin dermis and epidermis of dogs. There are many causes of canine dermatitis. It can be roughly divided into: mechanical, chemical, fungal, parasitic, and allergic factors. Dermatitis in dogs is an inflammation of the skin dermis and epidermis of dogs.
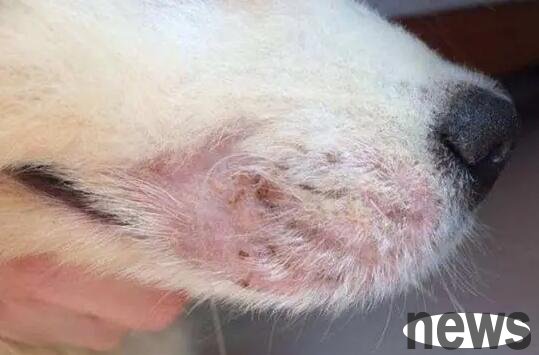
1. Causes of canine dermatitis: There are many causes of canine dermatitis. It can be roughly divided into: mechanical, chemical, fungal, parasitic, and allergic factors. 1. Mechanical: traumatic dermatitis, scalds, frostbite, radioactive damage, etc. caused by neck ring abrasions, autologous contusions, scratches, etc. 2. Chemical properties; chemical bath agents, apply irritating drugs, and long-term irritation of purulent secretions. 3. Fungal; microsporidium, gypsum-like microsporidium, and phytoniae. 4. Parasitic nature; such as demodex, scabies, cicadas, lice, flea, schistosomiasis, hookworm, etc. 5. Food allergies and drug allergies can lead to the occurrence of dermatitis.
2. Key points for diagnosis of canine dermatitis: 1. The dog's skin is red and swollen in flakes, stripes or indefinite shapes. When it seeps, it may be covered with a skin. When the skin is damaged, it may be erosion or ulcers, and there may be local pain and itch. 2. When a large amount of inflammatory exudates on the skin are covered with chronic dermatitis, skin hair can be seen falling off. The peptide thickens and has chapped. 3. When suffering from fungal dermatitis, the affected area will lose hair, and there will be white powder-like scabs on the spot, and there will be red protrusions under and around the scabs. 4. When suffering from parasitic dermatitis, red rash-like nodules can be seen on the head, back and abdomen, with yellow scabs on the surface, hair removal and severe itching.
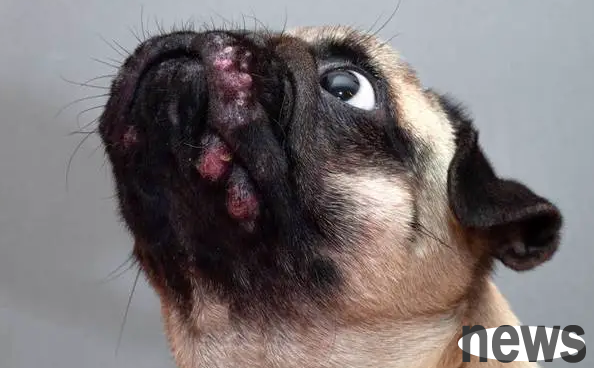
III. Prevention and treatment measures for canine dermatitis:
1. Desensitization and analgesic: oral or intramuscular corticosteroids, 1 mg/kg of body weight of ponnisone, 0.15-0.25 mg/kg of body weight of dexamethasone. 2. Apply sulfonamide ointment locally. 3. For chronic dermatitis, you can use deinflammatory ointment or hydrogen acetate ointment. 4. Fungal dermatitis can be applied with clotrimazole ointment, ringworm ointment or Dakkening ointment. 5. For skin parasitic dermatitis, refer to the treatment of demodex.
6. For dermatitis with bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy can be used systemically, and intramuscular injection of penicillosol or gentamicin, 2 times per day.